T-Shirt Fabric Guide: Everything You Need to Know
It’s no secret that we love a good t-shirt. This wardrobe staple is recognized for both its comfort and ability to express an idea, a logo, or a message through decoration and design. Did you know that different t-shirt fabrics are best suited to different types of projects and wear? Choosing the wrong fabric could mean accidentally botching a craft project, not wearing the best type of fabric for the weather, or realizing too late that the new shirt you just bought online is not as soft as expected.
In this guide, we’ll give you the low-down on the different types of t-shirt materials, the best use cases for each type of t-shirt material, their levels of softness, and even how different types of designs may look on them.
Important T-Shirt Fabric Definitions
Before we dive into more specific t-shirt fabrics and all of the cool techniques you can use to personalize them, let’s set the table with some important t-shirt fabric definitions to help you get familiarized with commonly used terms.
-
-
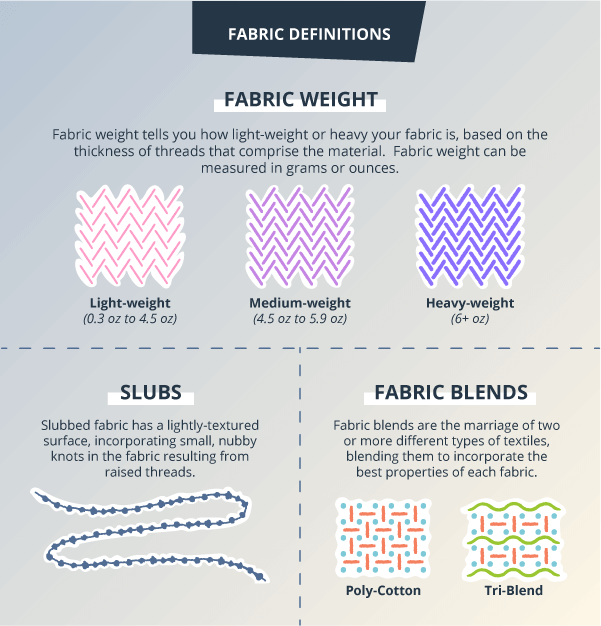
Fabric Weight: What is fabric weight? Fabric weight tells you how light-weight or heavy your fabric is, based on the thickness of threads that comprise the material. Fabric weight can be measured in grams or ounces.
- Light-weight fabrics can weigh between 0.3 oz to 4.5 oz, and include cotton, silk, chiffon, chambray, and linen, among others. Think of these as summer-y fabrics you may wear while enjoying an outdoor BBQ or stroll along the beach.
- Medium-weight fabrics may weigh between 4.5 oz to 5.9 oz. Some examples of medium-weight fabrics include polyester, nylon, or jersey knit. In terms of seasonality, many medium-weight fabrics can be comfortably worn year-round. They’re light enough to wear during summer, perfect for spring and early fall weather, and – with a little layering – work just as well for winter.
Heavy-weight fabrics weigh over 6 oz. These thicker fabrics include denim, corduroy, and flannel, to name just a few. Heavy-weight fabrics such as flannel and corduroy are cozy for winter months, however, the cotton-composition of denim, while heavier in terms of weight, still makes it breathable enough for all-season wear.
Fabric Blends: Fabric blends are the marriage of two or more different types of textiles, blending them to incorporate the best properties of each fabric. When you’re talkin’ t-shirts, some of the most popular blends include cotton-polyester blends, as well as tri-blend t-shirt fabrics, which are a mix of polyester, cotton, and rayon fibers. These blends allow for the breathability of natural cotton fibers mixed with the shrink-resistance of synthetic polyester, and the softness of rayon.
- Slubs: What are slubs? Sometimes referred to as “slub yarn” or “slub knit,” slubbed fabric has a lightly-textured surface, incorporating small, nubby knots in the fabric resulting from raised threads. While, historically, slubbed fabric was the result of imperfections and flaws in the weave of a given textile, today, fabric fans have come to love the slub, as it gives character to a fabric and offers a refreshingly unrefined, casual character to a t-shirt or piece of apparel.
Most Common T-Shirt Fabric Blends
When it comes to t-shirts, there are many different fabrics and fabric blends available. Each one offers its own distinct feel and benefits. Here are some of the most common fabrics and fabric blends you’ll encounter when shopping for t-shirts.
-
-
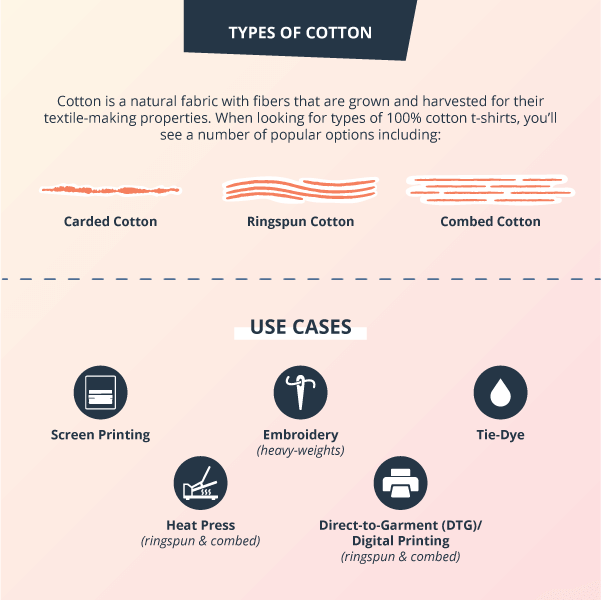
Types of Cotton
Cotton is a natural fabric with fibers that are grown and harvested for their textile-making properties. When looking for types of 100% cotton t-shirts, you’ll see a number of popular options including:
- Carded cotton is often the most economical choice. This cotton is spun (or “carded”) to transform it into fibers that can be made into a piece of fabric. Depending on the origin and length of the fibers that make up a piece of 100% cotton cloth, it determines the softness and refinement of the fabric.
- Ringspun cotton fits the bill as being stronger, smoother, and softer than carded cotton due to the way it’s processed.
- Combed cotton is the softest, smoothest, and most refined of cotton fabrics. While all cotton is spun or carded, not all cotton is combed. Rather, this is an added step in the refinement process. After the cotton has been spun, the cotton is then combed to further refine the strands and remove any imperfections, making a piece of combed cotton gloriously soft.
Regardless of the way it’s processed, cotton is highly breathable and easy to care for. However, it can fade over time, which can provide a vintage or well-worn cotton t-shirt look.
Pro Tip: Always read the care instructions on your fabric label—especially when it comes to cotton. Check the care label to see if your cotton shirt is pre-shrunk, or if the shirt may shrink slightly after a wash-and-dry cycle.
-

-
Polyester vs. Cotton
While both cotton and polyester are breathable and soft, there are some key differences between the two fabrics. Synthetic polyester is more of a light-weight fabric compared to cotton and dries faster if you get it wet. It also has a smoother, silkier feel, but is also clingier and slightly less breathable than natural cotton.
One key advantage of polyester is that it can be used to create moisture-wicking garments that pull sweat away from the body. On the flipside, cotton absorbs sweat and moisture and takes a longer time to dry. As a result, it may cling to the skin when wet compared to more moisture-resistant polyester.
Polyester is often used in moisture-wicking, high performance shirts on its own, but it's also a key component of poly-cotton blends, as well as tri-blend t-shirts that are a combination of cotton, polyester, and rayon.
-
-
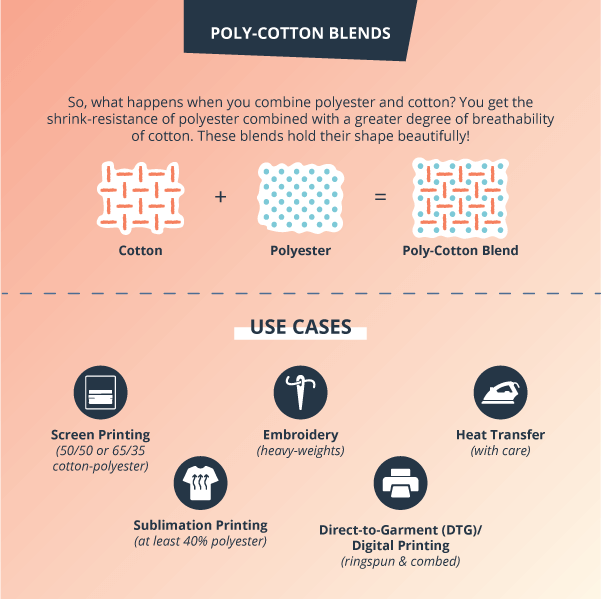
Poly-Cotton Blends
So, what happens when you combine polyester and cotton? You get the shrink-resistance of polyester combined with a greater degree of breathability of cotton. These blends hold their shape beautifully—even when they’re fresh out of the dryer! A polyester-cotton blend can also give your t-shirts a bit of extra stretch for a more flattering fit and has a softer hand, as well.
-
-
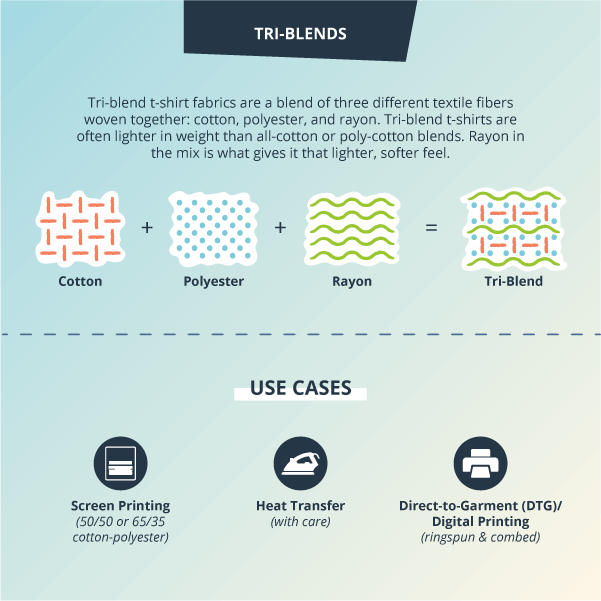
Tri-Blend vs. Cotton
Tri-blend t-shirt fabrics are a blend of three different textile fibers woven together: cotton, polyester, and rayon. Tri-blend t-shirts are often lighter in weight than all-cotton or poly-cotton blends. Rayon in the mix is what gives it that lighter, softer feel.
While cotton is a natural fabric and polyester is a synthetic material, rayon is a semi-synthetic fabric made from cellulose fibers derived from wood pulp. These fibers are then chemically treated to transform it into the versatile fabric you know and love. Like cotton, rayon is breathable; but similar to polyester, it dries faster than cotton.
Tri-blend t-shirt materials have an ultra-soft feel that has added stretch compared to all-cotton t-shirts. They cling in the right places and can offer a flattering fit with added breathability thanks to the looser weave. This looser weave gives tri-blend t-shirts more of a “distressed” or heathered look, especially when you print a design on your shirt. The properties of tri-blend fabric offer more of a vintage look that can give the piece more of a lived-in feel, even if it’s brand new.
-

-
Viscose (Bamboo)
One type of rayon fabric is viscose. This versatile textile is incredibly soft and is a chameleon among fabrics, with the ability to mimic the look and feel of cotton, polyester, or even silk. Viscose is also a semi-synthetic fabric made from bamboo wood pulp and treated with chemicals to process it into fibers that can be made into a soft, breathable fabric. Viscose, being a semi-synthetic fabric, is similar in terms of the breathability of cotton, but has the wicking properties and lighter feel of polyester.
-
-
Recycled Fabrics
A growing trend within the textiles industry, recycled fabrics (sometimes called “recovered fabrics”) are the result of using old fabric scraps or old articles of clothing to be reprocessed into new materials. Instead of producing new textiles from non-renewable resources, recycled fabrics aim to reduce the carbon footprint involved in making some types of fabrics.
First, previously-loved fabrics or articles of clothing are sorted by material and the condition the fabric is in, among other characteristics. Then those fabrics are shredded and transformed into fibers that are able to be mingled with new fibers in order to create an entirely new fabric or garment from recycled materials.
Now that you know more about some of the more common t-shirt materials, let’s hop into some of the different processes used to personalize those shirts and which fabrics work best with each method.
Best T-Shirts for Screen Printing
There is no single best fabric for screen printing. Actually, there are a variety of fabrics that work well to create screen printed shirts. Overall, the best t-shirt fabric for screen printing is cotton, although cotton-polyester t-shirt blends and tri-blend t-shirt materials can work just as well within this process, as long as you take the proper precautions.
The type of ink you use for screen printed t-shirts also plays a role in choosing the best fabric for your project. Water-based inks require a higher percentage of cotton in a poly-cotton or tri-blend t-shirt in order for them to properly adhere to the fabric. Adding a base layer of ink can help mitigate this problem, producing a more vibrant screen print. For darker shirts, Plastisol inks can produce vivid colors without worry of absorption or base layers. This type of ink is made from PVC polymer that sits on top of the fabric, as opposed to absorbing into the fabric the way a water-based ink does.
Screen printing (sometimes known as “silk screening”) deposits ink onto a shirt in a desired pattern, creating an eye-catching design. Typically, this method of printing works best when using only one or two colors of ink. Screen printing is done by hand, making this a more painstaking process than a machine-based process like direct-to-garment (DTG printing).
With screen printing, a mesh screen with the reverse image of a design is placed on top of a t-shirt. Ink is then rolled over the top of the screen and seeps through the screen so that it’s deposited in the correct areas to bring the printed design to life. Once the ink is deposited, the shirt is then exposed to a heat process to cure and set the ink. While tri-blend shirts can scorch easily during the curing process, experienced printers will adjust the oven temperature and slow the belt to ensure no scorching occurs.
-
What to Look For:
- Look for pre-shrunk cotton fabrics before screen printing to maintain the integrity of your design.
- Look for smoother weaves of cotton – such as ringspun and combed cotton. This gives you a smoother surface that allows ink to produce a crisper, truer image.
- Look for a higher percentage of cotton in poly-cotton or tri-blend shirts when using a water-based ink for better adherence to the fabric, resulting in sharp, clean colors.
- Look for cotton-polyester blended fabrics with a smooth weave. The wrinkle-resistant properties of either a 50/50 or 65/35 cotton-polyester blend make it easy to transfer the ink to the shirt for a smooth application.
- Look for heathered fabrics or garment dyed styles for a distressed, vintage feel of your screen printed graphic.
- Look for water-based inks if you want a softer hand on screen printed graphics.
- Look for Polymer-based inks (like Plastisol) to use on darker shirts for a more vibrant screen printed image
-
What to Avoid:
- Avoid more open weave cotton fabrics like carded cotton, which are often rough and uneven, making it more difficult to produce a quality screen print.
- Avoid 100% polyester shirts for screen printing if you are unfamiliar with the curing process needed for this material. These fabrics can bleed during the screen printing process and may not hold up well under the heat of the curing process. If you do want to print on a 100% polyester athletic t-shirt, be sure that your printer is knowledgeable about proper curing techniques on that material to avoid a scorched shirt.
- Avoid water-based inks on darker fabrics where absorption into the fabric could make it difficult to see designs. This can be prevented, however, by using a base layer to make the ink pop.
- Avoid Plastisol inks if you want to retain breathability across the surface of the fabric where the ink is used. Plastisol creates vivid colors and sharp lines, but if retaining the breathability of your tee is top-of-mind, this synthetic PVC ink can sit on top of the fabric, making it less breathable when wearing.
Best T-Shirts for Tie-Dye
Tie-dye t-shirts make a statement. They’re colorful, they’re cool, they’re one-of-a-kind, and are equally at home while grooving to your favorite jam band as they are featured in the social feeds of your favorite influencers. Making your own tie-dye t-shirt also conjures up memories of fun at-home projects or summer camp activities.
Tie-dye, as a process, involves twisting a t-shirt in a specific way and securing it with rubber bands to make a pattern. From there, the twisted tee can be squirted with different colors of fiber-reactive dye, or dip-dyed in a basin for an ombre effect.
The beauty of tie-dye is that you can use as many – or as few – colors as you like. You can even use bleach to “reverse tie-dye” a darker colored shirt and lighten the portions of the shirt that aren’t adhered with a rubber band.
The best material for tie-dye is cotton or another natural fabric. Because tie-dye requires a dye or bleach to seep into the threads of a shirt, natural fabrics that readily absorb moisture are your best bet. Overall, cotton t-shirts are the top choice for a tie-dye t-shirt project. Other cotton-based fabrics like denim and canvas can also be easily dyed using this method. Semi-synthetic fabrics like rayon and viscose can also offer you a vibrant tie-dyed t-shirt.
The fabric that will be most difficult to tie-dye is polyester. Tie-dyeing polyester t-shirts (using the traditional fiber-reactive dye method or the reverse-dye bleaching method) can often yield unpredictable results for a DIY project. Special dyes are needed as polyester does not absorb color as well as cotton or rayon.
-
What to Look For:
- Look for plain white shirts so that your dye colors have a blank canvas to make those colors pop if you plan to do a more traditional tie-dyed style.
- Look for natural or semi-synthetic fabrics like cotton, viscose, or rayon to better accept fiber-reactive dye and give you a vibrant display of colors.
- Look for darker colored cotton or rayon t-shirts if you plan to use the bleaching method to reverse tie-dye your shirt. While bleach can work to tie-dye polyester shirts, the results are often unpredictable.
-
What to Avoid:
- Avoid fabrics that are 100% polyester or have a high content of polyester. Polyester does not readily accept dyes as this synthetic fabric is significantly less absorbent compared to cotton and other natural or semi-synthetic fabrics.
- Avoid fabrics that are 100% polyester or have a high content of polyester. Polyester does not readily accept dyes as this synthetic fabric is significantly less absorbent compared to cotton and other natural or semi-synthetic fabrics.
Best T-Shirts for Embroidery
T-shirts with embroidered designs give a tactile feel and a distinctive touch. Whether your shirt features an embroidered logo or a fun, colorful design, this process can (literally) elevate the design elements of your t-shirt.
As a process, embroidery involves using a needle and thread (or embroidery yarn) to weave a raised design onto fabric. Because a t-shirt may need to withstand the poking and stretching required to create a woven design, the best t-shirts for embroidery will be those made from thicker, smoother, and more tightly-woven fabrics like a heavier-weight cotton or a poly-cotton blend.
Fabrics that have less stretch or give to them, such as 100% cotton, are another consideration for embroidered t-shirts. If a fabric is too stretchy, it can warp or distort your design. Embroidered designs require fabric to be tensely pulled in order to weave the design into the fabric. If you embroider a stretchy or ribbed fabric, the woven design may look very different when the fabric springs back to its un-stretched form.
When it comes to embroidered t-shirts, it’s best to avoid thinner, more delicate fabrics like rayon and lighter-weight cotton t-shirts. These fabrics may be prone to tearing as a result of the embroidery needle passing through the fabric repeatedly to stitch your design. Stick to sturdier cottons without a lot of give as your best bet to create a beautifully woven embroidered t-shirt.
-
What to Look For:
- Look for heavier cotton or poly-cotton t-shirts between 5.3 - 7.5 oz with a smoother, tightly-woven blend for an even application of embroidery. Although shirts in the 5 oz fabric weight range technically can be classified as medium-weight fabric, they will still be thick enough to support an embroidered design.
- Look for t-shirts that don’t have a lot of stretch to them. This ensures you retain the integrity of your embroidered design.
-
What to Avoid:
- Avoid thinner fabrics like rayon or light-weight cotton (under 5 oz), as they may tear under repeated stress of the embroidery needle.
- Avoid stretchy fabrics, as this can distort the finished product of your embroidered design.
- Avoid ribbed fabrics, which can also be on the stretchy side and compromise your stitching.
Best T-Shirts for Heat Press
For a more colorful design, bring the heat! Heat press, that is. Heat press (or heat transfer) printing involves transferring a vinyl design with adhesive backing onto a shirt, using heat and pressure to adhere the graphic. Unlike screen printing, which typically works best with only one or two colors, heat press designs allow you to add more colors to the mix for a visually striking graphic tee.
Once again, cotton t-shirts are the best choice for heat transfer graphics. Ringspun cotton and combed cotton with a finer, tighter weave provide an ideal surface for the heat transfer to adhere to. Shirts made from a cotton-polyester blend or tri-blend can accept heat transfer graphics, but you’ll need to be careful because synthetics like polyester and rayon can scorch under a heat press. Professional printers will know the proper way to adhere heat transfer graphics to a cotton-poly or tri-blend shirt to minimize the risk of burning the fabric in the process.
-
What to Look For:
- Look for ringspun or combed cotton t-shirts that can more easily accept a heat transfer graphic thanks to a smoother surface.
- Look for a professional that specializes in heat transfer designs if you would prefer this style of printing on either a cotton-polyester blend or tri-blend t-shirt. They’re aware of best-practices involved and can ensure your t-shirt isn’t scorched in the process. Many t-shirt printers and suppliers often have cheat sheets on-hand to ensure they are using best practices for time and temperature settings for heat press on a variety of fabrics. So, don’t feel you’re limited solely to one type of fabric or another! Rather, consult with your printer to get a feel for their knowledge.
-
What to Avoid:
- Use caution with 100% polyester shirts when using the heat press process. Take special care when using fabrics with a synthetic blend, such as cotton-polyester tees, as well as tri-blend tees that include polyester and rayon in their make-up. If applied incorrectly, your t-shirt may be damaged and scorched during the heat transfer process. Be sure to do the research on specific settings for both the machine itself, as well as how settings apply to various fabrics.
Best T-Shirts for Sublimation Printing
While sublimation printing might seem like magic, there’s quite a bit of science behind this method that’s gained popularity in recent years. Similar to heat transfer graphics, sublimation printing involves printing an image onto a special type of paper called (wait for it) sublimation paper.
However, unlike the heat transfer process, which adheres a decal-like vinyl image to a shirt using a heat press, sublimation printing involves using heat to transform the water-based ink from the sublimation paper into a gas that bonds to the fabric of the shirt itself instead of just resting on top of it. This produces a long-lasting design that won’t crack or peel with repeated wear like some heat transfer graphics.
Sublimation printing works better on lighter colored fabrics, as it can be difficult to see the transfer on a darker background. While you can print on colored fabrics, it’s important to be mindful that color may fade over time, diminishing the integrity of the design. For this reason, white or light pastel colored fabrics work best for sublimation printing.
The best fabric for sublimation printing is polyester and poly-cotton t-shirts with at least 40% polyester in their composition. Natural fibers, such as cotton, do not work well with sublimation printing. The sublimation process and dyes used aren’t able to bond with all-cotton fabric. While the image may temporarily transfer, the dyes can quickly wash off of cotton, leaving you with a sad, imageless t-shirt.
-
What to Look For:
- Look for polyester t-shirts or poly-cotton blends with no less than 40% polyester content.
- Look for white or light pastel colored t-shirts to apply sublimated designs. This will allow your colors to show more vividly against a lighter background.
-
What to Avoid:
- Avoid 100% cotton t-shirts as sublimation dyes won’t form a permanent bond with natural cotton fibers.
- Avoid attempting sublimation printing on darker t-shirts as your design will not be visible, or will become less visible over time.
Best T-Shirts for Direct-to-Garment (Digital Printing)
When you want a photorealistic image that captures every nuance of color and shading, direct-to-garment printing (sometimes referred to as “digital printing” or simply “DTG”) can help you replicate that imagery onto a t-shirt.
Similar to sublimated printing, DTG printing involves embedding the ink directly into your shirt. However, instead of using heat to evaporate the ink into the fabric, colors are deposited directly onto your shirt via a giant printer capable of producing millions of colors to create your image.
The best fabric to use for direct-to-garment DTG printing are 100% combed or ringspun cotton with a smooth, fine weave. DTG printing can also work on poly-cotton or tri-blend t-shirt materials that are at least 50% cotton. (Please keep in mind that DTG printing on tri-blend shirts will also produce a more weathered, distressed look instead of the more vibrant results you’d get with a 100% cotton tee.) DTG printing can be used on either light or dark t-shirt fabrics to produce striking imagery. The key is making sure you have the right type of fabric that readily accepts DTG ink and adheres to the fabric.
While DTG printing can look great on darker fabrics, there may be a few extra steps you’ll need to take in order to ensure your image looks sharp. A pre-treatment solution should be applied to the area where you’ll print your image onto the shirt. This pretreatment solution fills in any gaps in the weave to make the fabric smoother and easier to print on – which is especially important when using white ink on a dark colored shirt. This solution also partially cures the ink, allowing it to set.
Another step you may need to take when using DTG printing on darker fabrics is to print colors on a white base. Once the pre-treatment solution is applied, you can then layer on white ink before adding a final layer of colored ink to create your design.
-
What to Look For:
- Look for shirts made from 100% combed or ringspun cotton with a smooth, fine weave, or poly-cotton or tri-blend t-shirts that contain no less than 50% cotton content.
- Look for pre-treatment of darker fabrics before submitting them to the DTG printing process. This will help fill in any gaps in the weave and allow a base layer of white ink to partially cure before adding colored inks. This helps ensure your colors pop.
-
What to Avoid:
- Avoid using DTG printing on synthetic fabrics or fabrics that are less than 50% cotton.
- Avoid using too much or too little pre-treatment solution on darker fabrics. Too little can produce a dull image, while too much will wipe out your DTG image after washing.
Best T-Shirts for Mixed Media
What is a mixed media t-shirt project? Simply put, it’s any type of t-shirt that combines two or more design applications onto a single t-shirt. Maybe you want to embroider a direct-to-garment printed t-shirt. Or perhaps you want to use heat press graphics on a tie-dye t-shirt. Mixing-and-matching these approaches results in a mixed media style t-shirt.
There is no one single best fabric for creating a mixed media t-shirt. Rather, it depends on which techniques you want to apply to your design. In order to create a mixed media shirt that actually looks good, it’s best to take into consideration the unique properties of the material of the shirt you plan to use, as well as the characteristics involved with each process. By seeing where they overlap (and where to proceed with caution), you’ll wind up with a unique mixed media t-shirt design you’ll love.
With that in mind, if you’d wanted to create an eye-catching sublimated tie-dye t-shirt, you’d start by printing an image on a polyester or poly-cotton tee with at least 40% polyester makeup. From there, you could use bleach over a sublimated design to either create a worn, distressed look or use rubber bands for a more traditional tie-dye look. While this technique can be used after a shirt has been sublimated, you can also bleach a polyester or poly-cotton tee before sublimation printing to create a brighter, more vibrant look.
-
What to Look For:
- Look for shirts that combine the unique properties needed for two or more design applications.
- Example: Look for a 100% polyester (or no less than a 40% poly blend) t-shirt if you want to bleach a shirt with sublimated printing.
-
What to Avoid:
- Avoid fabrics that may work for one and not the other type of design application you may want to execute.
- Example: While ringspun or combed cotton may be ideal for screen printing, it may not work well for embroidery projects if it’s a thinner, finer weave.
-
Threadsy has all the fabrics you need!
Creating custom t-shirt designs can be a fun and exciting process. The first step in bringing your designs to life is getting familiar with the different types of fabrics and how they play into the design process.
From ultra-soft tri-blend tees to cool 100% cotton t-shirts, Threadsy has a wide selection of shirts to get you started on designing a t-shirt you’ll love to wear for years to come. While we hope this guide is a helpful starting point, if you have any questions about what fabric or style suits your project best, get in touch with us! We’d love to help you narrow down the field and find the right shirt for your next great t-shirt adventure!









